High blood pressure, often referred to as the “silent killer,” stealthily creeps into our lives, often without any noticeable symptoms. It’s a health concern that affects millions worldwide, leading to severe complications like heart disease and stroke. Understanding and monitoring your blood pressure is not merely a precautionary measure; it’s an active step toward safeguarding your well-being.
The Role of Accurate Blood Pressure Monitors in Healthcare
Imagine having a reliable companion that empowers you to take charge of your cardiovascular health – that’s precisely the role accurate blood pressure monitors play in modern healthcare. These devices have evolved beyond mere gadgets; they are pivotal tools enabling individuals to track and manage their blood pressure effectively. In a world where precision matters, these monitors stand as sentinels, providing valuable insights into one’s cardiovascular health and aiding in the early detection of potential risks.
As we learn the intricacies of choosing the right blood pressure monitor, let’s unravel the significance of this seemingly routine yet profoundly impactful practice.
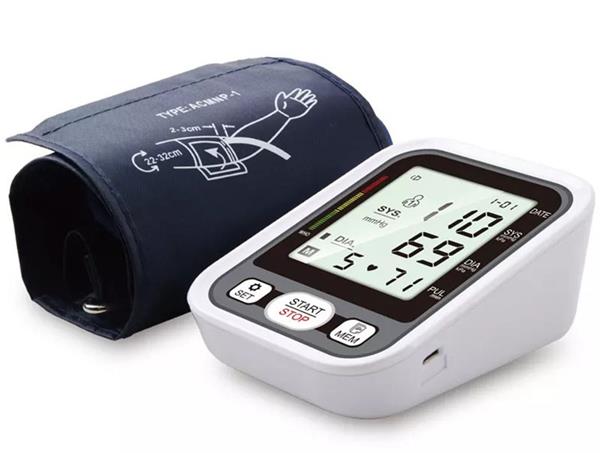
Understanding Blood Pressure
A. Explanation of Systolic and Diastolic Pressure
To grasp the essence of blood pressure, we must decode the intricate language of systolic and diastolic pressure. Imagine your circulatory system as a bustling network – systolic pressure denotes the force exerted on arterial walls during the heart’s contraction, propelling blood into the arteries. Conversely, diastolic pressure represents the residual force during the heart’s relaxation phase, reflecting the constant pressure within the arteries. Expressed as a ratio, such as 120/80 mmHg, these values paint a detailed picture of cardiovascular health.
When you engage a blood pressure monitor, you embark on capturing this rhythmic ballet – a choreography of the heart’s dynamic movements. Understanding these numerical values becomes crucial in deciphering the cardiovascular symphony.
| Blood Pressure Level | Blood Pressure Value |
| Grade I Hypertension | 140/90~159/99mmHg |
| Grade II Hypertension | 160/100~179/109mmHg |
| Grade III Hypertension | 180/110mmHg and above |
B. Normal Blood Pressure Ranges
Let’s navigate the spectrum of “normalcy” in blood pressure, acknowledging that the once widely accepted 120/80 mmHg standard has undergone a paradigm shift. Optimal blood pressure, now categorized differently, resides below 130/85 mmHg. Mild variations within the healthy range are permissible, but persistent elevations may indicate potential risks. As the numbers fluctuate, the urgency for proactive monitoring intensifies, emphasizing the importance of your blood pressure meter as a vigilant observer.

C. The Significance of Regular Monitoring
Regular blood pressure monitoring transforms into a personal health checkpoint, akin to routine maintenance for your body’s engine. In light of the revised standards, a reading above the traditional 120/80 mmHg doesn’t necessarily flag hypertension. The digital blood pressure monitor becomes an essential ally, offering not just numerical readings but empowering you with insights into your circulatory health.
Embrace regular monitoring as an ongoing conversation with your cardiovascular system. The new standards, now set at 130/85 mmHg for optimal blood pressure, redefine the dialogue between you and your health. It’s a proactive stance against the unforeseen, unraveling patterns and trends that guide informed decisions. As we navigate the landscape of blood pressure awareness, let’s adapt to the evolving standards and wield the tools that empower us in our journey to well-being.
Types of Blood Pressure Monitors
A. Manual Blood Pressure Monitors
Description of Manual Devices:
Manual blood pressure monitors, often recognized by their traditional sphygmomanometer and stethoscope setup, require a hands-on approach. Users manually inflate the cuff around the upper arm, using the stethoscope to listen for the pulsation sounds in the brachial artery. This method provides a direct and tactile connection to the measurement process.
Pros and Cons of Manual Blood Pressure Monitor:
Pros:
Accuracy: Manual monitors are known for their precision in blood pressure measurement.
Cost: Generally more affordable compared to automatic counterparts.
No batteries or power source is required.
Cons:
Skill-dependent: Proper use relies on the user’s proficiency in cuff inflation and auscultation.
Time-consuming: Manual monitoring may take longer compared to automated methods.
Requires training: Users need training to achieve accurate results.

B. Automatic Blood Pressure Monitors
Overview of Automatic Devices:
Automatic blood pressure monitors, also known as digital blood pressure meters, have gained popularity for their ease of use. These devices typically consist of an inflatable cuff, an automatic inflation system, and a digital display. Users only need to wrap the cuff around the upper arm, and the device takes care of the rest, providing quick and convenient readings.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor:
Advantages:
User-friendly: Automatic monitors are easy to use, making them accessible for individuals of all ages.
Quick and convenient: Automated measurements are faster compared to manual methods.
Memory functions: Many digital monitors store multiple readings for tracking trends.
Disadvantages:
Cost: Automatic monitors may be more expensive than manual alternatives.
Dependency on batteries or power source.
Potential for inaccurate readings due to movement or improper positioning.
C. Wrist vs. Upper Arm Blood Pressure Monitors
Comparison of Wrist and Upper Arm Monitors:
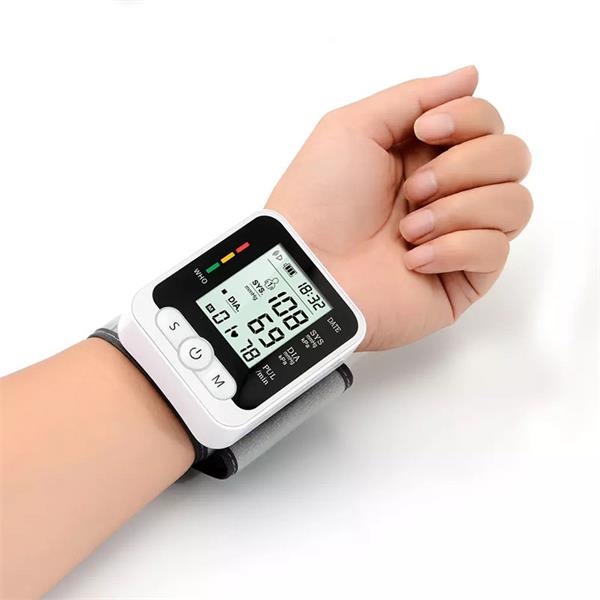

Wrist Blood Pressure Monitors:
Compact and portable.
Suitable for individuals with larger upper arm circumferences or mobility issues.
Positioning is critical for accurate readings.
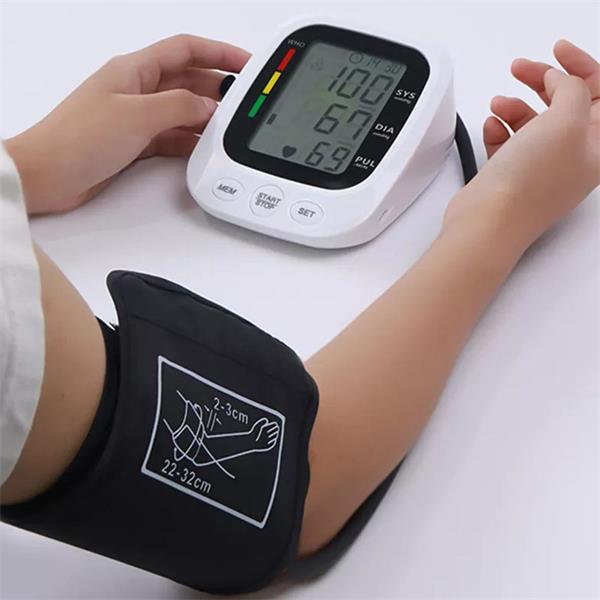
Upper Arm Wrist Blood Pressure Monitors:
Typically more accurate and recommended by healthcare professionals.
Require proper cuff sizing for precise readings.
Maybe bulkier but often more reliable.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Them:
Accuracy: Consider the level of precision required for your monitoring needs.
Comfort and Mobility: Assess your comfort and the convenience of using the monitor in different settings.
Healthcare Professional Recommendations: Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
Budget: Evaluate the cost implications of wrist and upper arm monitors.
In navigating the diverse landscape of blood pressure monitors, understanding the features and considerations associated with manual, automatic, wrist, and upper arm devices empowers individuals to make informed choices aligned with their unique needs.
Features of Blood Pressure Monitor to Consider
A. Cuff Size and Fit
Importance of the Right Cuff Size:
Achieving accurate blood pressure readings begins with the right cuff size. An improperly sized cuff can lead to inaccurate measurements, potentially impacting the assessment of your cardiovascular health. The cuff should snugly encircle the upper arm, neither too tight nor too loose, ensuring optimal contact with the skin and arteries.
How to Measure and Choose the Correct Cuff Size:
Measure the circumference of your upper arm at its midpoint.
Select a cuff size that matches your measurement, ensuring it falls within the recommended range provided by the blood pressure monitor’s guidelines.
Regularly check and adjust the cuff size, especially if there are changes in weight or muscle mass.
B. Digital Display and Readability
Importance of Clear and Readable Displays
The digital display of a blood pressure monitor serves as the gateway to understanding your cardiovascular health. A clear and easily readable display is essential for users to interpret their blood pressure readings accurately. Strive for a monitor with a display that provides well-contrasted, large fonts and backlighting for enhanced visibility in various lighting conditions.

Considerations for Users with Visual Impairments:
Choose a monitor with audible features, such as spoken results or sound cues, to assist users with visual impairments.
Opt for monitors with tactile buttons or distinctive markings for easier navigation by touch.
Ensure compatibility with external devices or applications that can provide audio feedback or transmit data to accessible platforms.
C. Memory and Data Storage
Benefits of Blood Pressure Monitor with Memory Functions:
Memory functions in blood pressure monitors offer a valuable advantage by allowing users to track their historical readings over time. This feature aids in recognizing patterns, identifying trends, and providing healthcare professionals with comprehensive data for more informed assessments.

How Data Storage Can Aid in Tracking Blood Pressure Trends:
Regularly review stored data to observe trends and changes in blood pressure.
Share historical data with healthcare providers during check-ups for a more holistic understanding of your cardiovascular health.
Utilize accompanying apps or software that may synchronize with the monitor for seamless data transfer and analysis.
D. Accuracy and Calibration
Significance of Accuracy in Blood Pressure Readings:
The credibility of blood pressure measurements hinges on the accuracy of the monitor. Reliable readings form the foundation for effective monitoring, diagnosis, and management of cardiovascular health.
Tips on Calibrating and Maintaining Accuracy:
Follow the manufacturer’s calibration guidelines to ensure consistent accuracy.
Regularly check and, if necessary, recalibrate the monitor according to the provided instructions.
Store and handle the monitor appropriately to prevent damage that could impact its precision.
In navigating the array of features available in blood pressure monitors, focusing on cuff size, display clarity, memory functions, and accuracy can enhance the effectiveness of your monitoring routine. These considerations collectively contribute to a more informed and reliable approach to managing your cardiovascular well-being.
User-Friendly Operation of Blood Pressure Monitor
A. Ease of Use for Different Age Groups
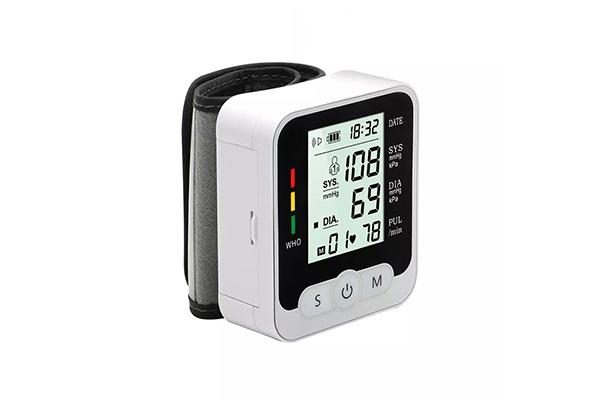

Considerations for Elderly Users:
Elderly individuals often require additional considerations when selecting a user-friendly blood pressure monitor. Opt for devices with:
Large, well-lit displays for easy readability.
Simplified button layouts and intuitive controls.
Adjustable and comfortable cuffs, accommodating potential mobility challenges.
Audible features or spoken instructions for users with visual or cognitive impairments.
Clear and straightforward instructions for setup and operation.
User-Friendly Features for All Age Groups:
User-friendly design extends beyond age-specific considerations to cater to a diverse audience. Look for monitors with:
Intuitive interfaces that guide users through the monitoring process.
Universal symbols and easily understandable indicators.
Comfortable cuffs that suit various arm sizes, ensuring a hassle-free experience for all users.
Multi-language support for a broader user base.
Consistent and prompt feedback, reducing the learning curve for new users.
B. Battery Life and Power Options
Overview of Power Options (Batteries, Adapters):
Blood pressure monitors commonly offer multiple power options to suit users’ preferences and lifestyles:
Batteries: Convenient for portability and travel. Ensure the monitor uses easily replaceable batteries for accessibility.
Adapters: Ideal for users who prefer a constant power source, eliminating the need for battery replacements.
Some models may offer both options, providing flexibility in usage scenarios.
Tips on Maximizing Battery Life:
Use High-Quality Batteries: Invest in reputable and long-lasting battery brands to maximize the monitor’s operational lifespan.
Turn Off When Not in Use: Power down the monitor when not actively monitoring to conserve battery life.
Regularly Check and Replace Batteries: Monitor the battery indicator and replace batteries promptly to avoid sudden power loss during use.
Use Rechargeable Batteries: If applicable, opt for rechargeable batteries to reduce environmental impact and long-term costs.
A user-friendly blood pressure monitor not only simplifies the monitoring process but also accommodates the diverse needs of different age groups. Considering ease of use, ergonomic design, and adaptable power options ensures a positive and inclusive experience for all users.
Recommendations and Reviews
A: Top Picks for Blood Pressure Monitors
a. JINYE Digital Blood Pressure Monitor:
This model from JINYE stands out for its precision and user-friendly design. Users appreciate its accuracy, especially when compared to more expensive alternatives.
The large, backlit display ensures readability in various lighting conditions, catering to users of all ages.
Its memory function allows individuals to track and store multiple readings, providing a comprehensive overview of their blood pressure trends.
b. JINYE Smart Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor:
JINYE’s Smart Wrist Monitor combines portability with advanced features. Users value its compact design, making it ideal for on-the-go monitoring.
Bluetooth connectivity allows seamless data transfer to smartphones, enabling users to share their readings with healthcare providers for remote monitoring.
The adjustable wrist cuff ensures a comfortable fit, accommodating various wrist sizes.

B: Recommendations Based on User Feedback and Expert Opinions:
a. User Feedback:
Positive user reviews highlight the ease of use and accuracy of JINYE’s blood pressure monitors.
Users appreciate the clear instructions provided, making the devices accessible to individuals of all technical backgrounds.
The durable construction and reliability of JINYE monitors have garnered praise for long-term usage.
b. Expert Opinions:
JINYE’s commitment to precision and innovation has earned recognition from healthcare professionals. Experts acknowledge the monitors’ adherence to accuracy standards.
The user-friendly interfaces and features cater to a broad spectrum of users, aligning with the evolving needs of modern healthcare.
C: Why Choose JINYE Blood Pressure Monitor:
Accurate Measurements:
JINYE’s blood pressure monitors are renowned for their precision, providing users with reliable readings crucial for effective monitoring and management.
User-Friendly Design:
The intuitive interfaces and ergonomic designs of JINYE monitors make them accessible to users of all ages and technical proficiency levels.
Innovative Features:
JINYE embraces innovation, incorporating features such as Bluetooth connectivity and memory functions to enhance the overall monitoring experience.
Durable Construction:
JINYE monitors are built to last, with durable materials ensuring longevity and consistent performance, even with regular use.
Comprehensive Customer Support:
JINYE is committed to providing excellent customer support, assisting users with any inquiries, and ensuring a positive experience with their blood pressure monitors.
In conclusion, JINYE’s blood pressure monitors stand out in the market due to their accuracy, user-friendly design, innovative features, durability, and comprehensive customer support. These qualities make them top recommendations for individuals seeking reliable tools for monitoring their cardiovascular health.